It is significant to note the difference between ERP and MRP because they serve different functions. Even though Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Material Requirements Planning (MRP) are both software systems used for managing the resources of a business.
While MRP is focused on the production process, ensuring that the right amount of materials are available at the right hour, ERP is a more comprehensive system that integrates all aspects of the business, including manufacturing, finance, and customer management.
Understanding the difference between MRP and ERP can help businesses choose the most appropriate software for their needs and improve their overall efficiency and productivity.
If you want to know more about ERP vs MRP, the benefits of MRP and ERP and more, do continue reading.
What Is ERP?
ERP or Enterprise Resource Planning is a software system that integrates and manages an organization's business processes in a unilateral platform. It provides a centralized database facilitating communication and collaboration across departments, enabling streamlined workflows, better decision-making, and increased efficiency.
ERP includes modules for finance, human resources, supply chain management, inventory management, customer relationship management, and more. An ERP tool can help organizations reduce costs, improve productivity, and gain a competitive edge by automating routine tasks and providing real-time data.
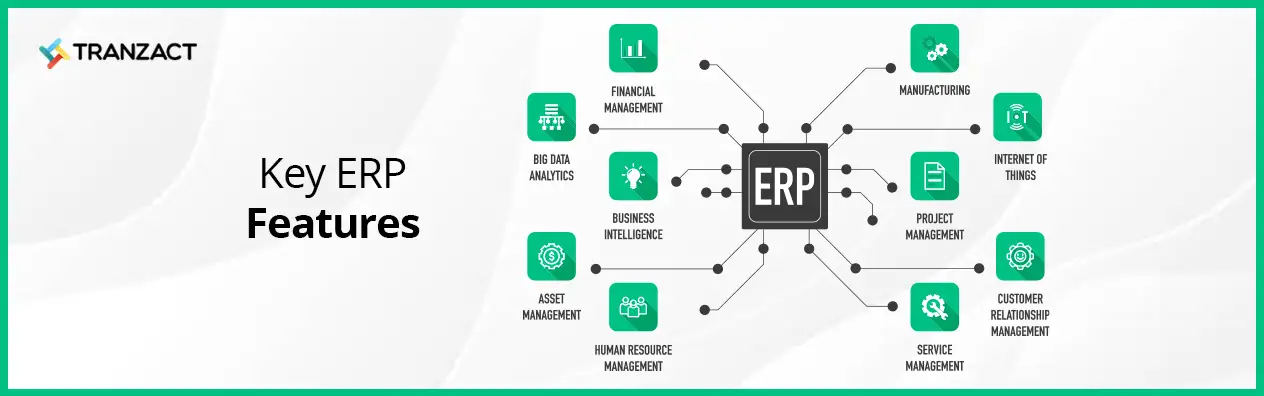
A. Functions of ERP
The functions of ERP include, helping organizations manage their core business processes and providing a unified and integrated platform that streamlines all aspects of a business's operations, from finance to production to supply chain management.
An ERP also ensures automation of routine tasks, reducing manual data entry, and eliminating silos of information that may exist across departments. This facilitates better communication and collaboration between different departments, leading to improved decision-making and greater efficiency. An ERP system provides real-time visibility into key performance indicators, enabling managers to monitor and analyze business performance at any time. It allows organizations to quickly identify areas that need improvement and make informed decisions based on accurate data. It assists businesses to streamline their operations, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity.
B. Benefits of ERP
ERP provides many unique benefits which can help organizations streamline their operations and improve their overall performance. Here are some advantages of ERP:
1. Increased Efficiency
An ERP system automates many manual processes and reduces the need for manual data entry, which helps organizations operate more efficiently. For example, an ERP system can automate order processing, inventory management, and financial reporting, reducing the time and resources required to complete these tasks.
2. Improved Visibility
ERP systems provide real-time visibility into various aspects of an organization's operations. It allows managers to track key performance indicators and make informed decisions based on accurate, up-to-date data.
An ERP system can also provide insights into areas like inventory levels, sales trends, and customer behavior, which can help organizations make more informed business decisions.
3. Better Collaboration
ERP systems provide a single source of truth for all business data, which can help improve collaboration across different departments and functions. For example, an ERP system can help sales teams coordinate with production teams to ensure that orders are delivered on time and in full.
4. Enhanced Customer Service
ERP systems can help organizations improve their customer service by providing better access to customer data and enabling faster response times to customer inquiries. This can help organizations build stronger relationships with their customers and improve customer satisfaction.
5. Improved Financial Management
An ERP system also supports organizations improve their financial management by providing real-time financial data and automating many financial processes. This can help organizations reduce the risk of errors and fraud, and ensure that financial data is accurate and up-to-date.
6. Scalability
ERP systems are designed to be scalable, which means they can grow and adapt to meet the changing needs of an organization. It makes an ERP system ideal for organizations looking to enter new markets or expand their operations.
C. Limitations of ERP
The ERP tool is powerful and can help organizations streamline and integrate their business processes. However, like any technology, ERP systems also have some limitations. Here are a few:
1. High Implementation Costs
An ERP system can be costly to implement, and the cost can vary depending on the size of the organization and the complexity of the system. The implementation process can also be time-consuming and disruptive to normal business operations.
2. Customization Challenges
ERP systems are designed to provide a standardized set of functions and features to all users. Customizing an ERP system to meet specific business needs can be complex and may require significant resources and expertise.
3. Complexity
ERP systems can get highly complex and can be difficult to understand and use. Training employees to use the system effectively can take time and resources, and even experienced users may encounter difficulties when working with the system.
4. Dependence on Vendor
Once an organization has implemented a manufacturing ERP software, it becomes highly dependent on the software vendor for support and upgrades. This can lead to vendor lock-in, where an organization is unable to switch to a different vendor or system without significant cost and disruption.
5. Data Security and Privacy Risks
ERP systems contain a vast amount of sensitive data about an organization's operations, employees, and customers. This data is vulnerable to theft and loss.
What Is MRP?
MRP or Material Requirements Planning is a computer-based resource planning system manufacturers use to plan and control the amount and timing of materials needed for production by analyzing sales forecasts, inventory levels, and production schedules.
It considers factors such as lead time, safety stock, and order quantities to ensure that the right material quantity is available at the right time to meet production needs while minimizing inventory costs. MRP helps manufacturers optimize their supply chain, improve production efficiency, and reduce waste, ultimately leading to higher profitability and customer satisfaction.
A. MRP I and MRP II
The MRP system offers two planning levels, MRP 1 and MRP 2.
MRP 1
MRP 1 is the basic level of planning that focuses on the materials needed for production in the short term. It involves calculating the quantities and delivery dates of raw materials, components, and other inputs needed to fulfill the production schedule.
MRP 1 is typically used by production planners to ensure that the necessary materials are available at the right time and in the right quantities to meet production demands.
MRP 2
Based on the objectives of MRP system, MRP 2 is a more comprehensive level of planning, which extends beyond the short-term and takes into account other factors such as capacity planning, sales forecasting, and inventory management. It involves using MRP 1 data as well as information about production capacity, lead times, and inventory levels to create a more accurate and holistic production plan.
MRP 2 is used by senior management to make strategic decisions about production, sales, and inventory levels.
B. Functions of MRP
The functions of the MRP system include:
Inventory Controlling:
MRP helps maintain an optimal inventory level by calculating the raw materials needed for production based on demand and lead times.
Production Planning:
MRP enables efficient production planning by generating schedules, identifying capacity constraints, and tracking progress against the plan. Bill of Material:
MRP uses the Bill of Material (BOM) to calculate the raw materials required for each product, making it easier to manage complex production processes.
Generating Purchase Order:
The MRP system generates purchase orders for raw materials based on the production schedule, ensuring timely delivery and reducing stockouts.
Allocating Resources:
MRP helps assign resources like machinery and labor to meet production demands and improve productivity.
Reducing Lead Time:
By accurately estimating the lead time for each component of a product, MRP helps reduce lead times, enabling faster response to customer demands.
Reducing Costs:
MRP can help reduce inventory carrying costs, stockouts, and overproduction, resulting in significant cost savings for businesses.
C. Benefits of MRP
There are many benefits of MRP, including simplified inventory management and better production planning. Some other advantages of MRP are as follows:
1. Increased Accuracy in Demand Forecasting
MRP uses historical data and sales forecasts to accurately predict future demand for materials, helping businesses plan and avoid costly production delays.
2. Improved Communication and Collaboration
MRP provides a platform for sharing data and collaborating with suppliers, ensuring that all parties are in accordance with each other and working towards a common goal.
3. Enhanced Supply Chain Visibility
MRP gives businesses greater visibility into their supply chain, allowing them to identify potential bottlenecks and risks and proactively address them.
4. Simplified Procurement
A Material Requirements Planning system streamlines the procurement process by automating the ordering of materials and supplies, reducing the need for manual data entry and paperwork.
5. Increased Flexibility
MRP allows businesses to quickly adjust production schedules and inventory levels in response to changing market conditions, customer demands, or other factors.
6. Improved Quality Control
MRP can help businesses ensure that materials and components meet their quality standards by tracking supplier performance, monitoring production processes, and conducting quality checks.
D. Limitations of MRP
While there are many benefits of MRP in manufacturing and production operations, there are a few limitations to consider:
1. Complexity
An MRP system can be complex and require a high level of technical expertise to implement and maintain, making it challenging for small businesses or those with limited information technology (IT) resources.
2. Data Accuracy
MRP relies heavily on accurate data to function effectively. Inaccurate data can lead to incorrect inventory levels, production schedules, and other critical information.
3. Cost
An MRP system can be expensive to implement, as it requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and training.
4. Implementation Time
Implementing an MRP system can be time-consuming, taking weeks or even months to fully integrate into a business's operations.
5. Resistance to Change
Implementing an MRP system may require changes to existing processes and workflows, which can meet resistance from employees who are used to working in a certain way.
Difference Between ERP and MRP
ERP and MRP are both software systems used to manage manufacturing and production operations. While there is some overlap between the two, there are a few major differences between ERP and MRP to consider:
1. Scope
ERP systems are broader in scope than MRP, encompassing a wide range of business functions, including finance, human resources, supply chain management, and customer relationship management. MRP, on the other hand, focuses specifically on material planning and inventory control.
2. Integration
ERP systems are designed to integrate multiple business functions into a single, unified system. While MRP software systems may integrate with other systems, they are typically standalone software solutions focused solely on material requirements planning.
3. Data Input
ERP systems rely on data from multiple sources, including suppliers, customers, and internal departments, to function effectively. MRP systems, by contrast, rely primarily on data related to material requirements and inventory levels.
4. Planning Horizon
ERP systems typically have a longer planning horizon than MRP, covering long-term strategic planning and short-term production planning. MRP systems, on the other hand, focus primarily on short-term production planning, typically covering a planning horizon of weeks or months rather than years.
5. Customization
ERP systems are often highly customizable, allowing businesses to tailor the system to their needs and processes. While MRP systems may offer some customization, they are typically less flexible in this regard.
6. Cost
ERP systems are typically more expensive than MRP systems due to their broader scope, greater complexity, and longer implementation times.
What Is the Relationship Between ERP and MRP?
When it comes to ERP vs MRP systems, it can be said that MRP is a subset of ERP. ERP systems typically include MRP modules to manage material planning and inventory control. In this way, MRP is integrated into the larger ERP system, providing a more comprehensive solution for managing manufacturing and production operations.
Does My Company Need ERP or MRP or Both?
Determining whether a company needs ERP, MRP, or both depends on several factors, including the company's size, the complexity of its manufacturing processes, and its goals for growth and expansion. You can take the following points into consideration while making a decision:
ERP may be the right choice in the following cases:
1. Substantial Company Growth
The company is growing and needs to manage multiple business functions, such as finance, human resources, customer relationship management, and supply chain management, in a single, integrated system.
2. Complicated Manufacturing Procedures
The company has complex manufacturing processes that require advanced planning and scheduling capabilities.
3. Collaboration
The company wants to streamline processes and improve collaboration between departments.
MRP may be the right choice in the following cases:
1. Optimization
The company has its focus on managing and optimizing its material planning and inventory control processes.
2. Simple Manufacturing Procedures
The company has simple manufacturing processes and does not require the breadth of functionality provided by ERP.
3. Affordability
The company is smaller and may not have the resources to invest in a comprehensive ERP system.
Both ERP and MRP may be the right choice if:
a. The company has complex manufacturing processes that require both advanced planning and scheduling capabilities, as well as material planning and inventory control. b. It wants to optimize its entire supply chain, from raw materials to finished goods.
c. The company has a high level of growth and needs a scalable system that can support its needs over time.
How to Choose the Best Software?
Choosing the best software for your business can be challenging, but there are several ways to make the process easier and more effective. Here are some tips:
Identify Your Business Requirements
Having a clear understanding of your business requirements will help you narrow down the list of potential software solutions and identify the ones best suited to your needs.
Research Available Options
Look for reviews, case studies, and other resources to help you understand how the software works and what other users think about it.
Evaluate the Features
Pay close attention to the software that is most important to your business. Consider how each software option will integrate with your existing systems and processes.
Consider the Vendor
When choosing software, look for a vendor with a good reputation, a strong support system, and a track record of success.
Look for Customization Options
If your business has unique needs or processes, look for software options that offer customization options. It allows you to tailor the software to your needs and workflows.
Consider the Cost
Finally, consider the cost of each software option, including the upfront cost and ongoing maintenance and support fees. Look for a software option that offers good value for money and fits within your budget.
Meet Your Business's ERP and MRP Needs With TranZact
TranZact offers a comprehensive suite of tools for managing a business's ERP and MRP needs. With its intuitive user interface, customizable modules, and powerful analytical capabilities, TranZact stands out as the best software solution for businesses looking to streamline their operations and improve their overall performance.
You won't need worry about the hidden difference between ERP and MRP modules as TranZact offers unmatched flexibility and scalability for all key functions including requirements planning, allowing you to tailor the software to your specific needs. With TranZact, you can automate and optimize your processes, improve inventory management, and gain valuable insights into your operations. TranZact is the best choice for an efficient and reliable ERP and MRP software solution.
FAQ on Difference Between ERP and MRP
1. Is MRP better than ERP?
Both MRP and ERP are important and impactful tools for managing manufacturing operations. Whether MRP or ERP is better depends on the needs and specific workflows of the business.
2. Is TranZact ERP or MRP?
TranZact is a cloud-based business automation software that offers ERP solutions to streamline everything from inventory, MRP to production.