ERP implementation life cycle is a top priority for businesses nationwide to manage their daily operations and boost profitability efficiently. The end-to-end lifecycle of ERP directly affects the proper execution of enterprise resource planning (ERP) and successful ERP deployment. With this blog, you will know all about ERP implementation, methodology, and ERP implementation phases in detail.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
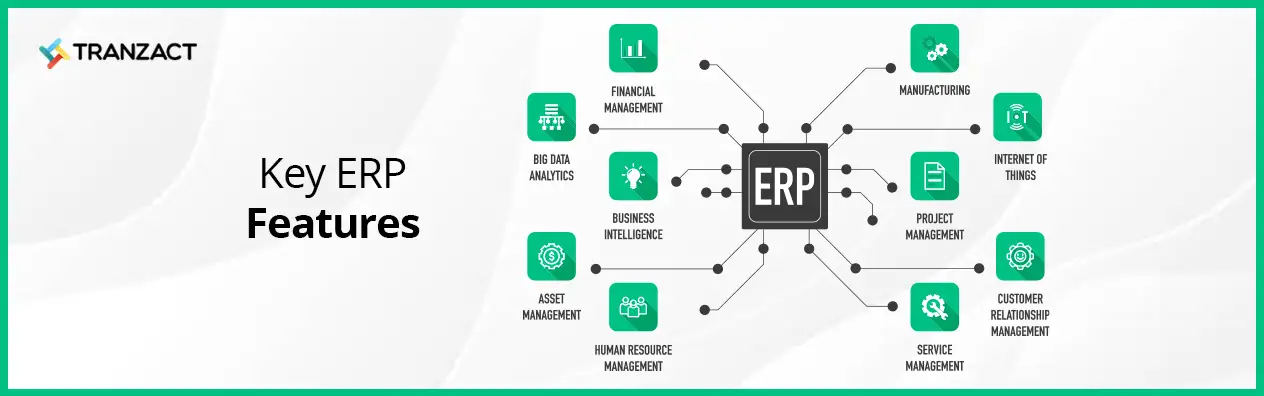
Enterprise Resource Planning, created in the 1990s, is the backbone of local and international operations, supporting most functional areas in daily operations. This type of software is popular among manufacturing business owners. Any task can be automated with enterprise resource planning (ERP). Every department's activities may also be easily managed using ERP by using a single database. It enables a quick, simple, and time-efficient method of working.
By facilitating and optimizing intra- and inter-enterprise collaborative operational and financial processes, ERP is a business strategy and collection of industry-domain-specific applications that create customer and shareholder communities value network systems. At its foundation, ERP is a powerful tool for using data management to centralize information and workflow procedures because ERP centralizes all of your workflow data.
ERP Implementation
Planning, setting up, and installing an ERP is called ERP implementation. Implementing a new ERP system is the most significant decision when it comes to the investment of time, finances, and resource commitment a company will ever make.
An ERP system connects several corporate operations, including financial management, human resources, sales, and manufacturing, to provide higher production and efficiency benefits. The procedure usually lasts a few months and needs to be straightforward because an ERP system supports and automates a wide range of complex operations.
The business must carefully define its needs, decide how to rework procedures to benefit from the system, set up the ERP system to support those processes, and rigorously test it before making it available to users if it is to be implemented successfully. It takes careful planning and a structured implementation strategy to complete all those tasks successfully and on time.
ERP software would be instantly ready to use and satisfy your functional requirements in a perfect world. But to suit your unique business demands, third-party software integrations or ERP customizations frequently need to be made. As a result, these extra factors may cause the ERP system deployment timeline to be extended.
Remembering that a successful ERP project requires more than just the software is also critical. Working with an experienced ERP installation partner who comprehends your company, can lessen the impact of technical challenges that will inevitably arise, and can use their experience to keep the project within scope and on the budget is equally crucial.
Implementation Methodology
The most important step of ERP implementation is selecting an implementation technique. Under the 'big bang' approach, the entire system is deployed across the organization by a predetermined deadline.
Manual or outdated systems are abandoned when everyone moves to the new system, and the integration is speedier and less expensive than a phased implementation. On the other hand, vulnerability is significantly raised, necessitating higher-than-average, albeit temporary, costs for testing, training, and support.
Another vital strategy is 'phased implementation,' which entails implementing changes gradually. This method takes longer, needs more focus, and necessitates continuing system maintenance. Yet, a slow rollout is safer, provides people more time to become familiar with it, and offers more accessible backup strategies.
Many ERP implementation phase choices include:
- A multi-location company's progressive location-based rollout
- Gradual adoption by each corporate division, such as human resources
The implementation technique should be developed after considering the available resources, the level of preparation, the perception of risk, the execution timetable, and the financial constraints.
Other crucial strategy issues:
- Gathering, removing, and filtering duplicate data associated with historical data.
- Adding to and updating current resources via software and hardware.
- Compatibility with the current operating system and database.
- Advocates for the project and a competency center.
The ERP implementation life cycle is a process that needs to be carried out correctly, and top management of the company needs to be involved in each step, starting with the ERP purchase and continuing with the involvement of the head of information technology (IT) and the head of the functional area of the company in the demo and business plan. Another key aspect to note is that the ERP software may have distinct objectives for those participating in the early stages than those who use it.
Phases of ERP Implementation Life Cycle
A typical ERP deployment plan has six phases with distinct goals. Companies differ from each other in terms of the phases, but generic phases of the ERP implementation life cycle contain:
1. Research and Planning
What stage of ERP implementation is the first? Researching and selecting a system, forming a team, and defining requirements for the system are all part of this process.
Implementation-related tasks will be handled by the project team, including developing the project plan, setting goal dates, ensuring enough resources are allocated, choosing products, and managing the project daily.
To understand the ERP implementation life cycle with an example, let's consider a business with multiple stakeholders. An executive sponsor, a project manager, and representatives from the departments using the system often make up the ERP project team. Senior management must be involved to help with system design and configuration; the team may also hire a third-party consultant or ERP implementation partner. Additionally, any internal experts who will assist in implementing the system should be included, such as an IT representative and a report writer.
When the firm clearly understands its requirements, the team may choose and purchase an ERP system during this phase. The business must also choose whether to employ an ERP system in-house or outside the cloud. In-house means you acquire and set up hardware and software for an on-premises system in your business' data center. Contrarily, cloud-based ERP is typically offered as an online subscription service, making it easier to adopt and requiring less internal IT expertise.
2. Style
Based on specific requirements and existing procedures, the design phase creates the detailed design of the new ERP system. This entails creating new, more effective workflows and other business procedures utilizing the technology. The design process should incorporate users because they are the ones who are most familiar with the current business procedures.
Engaging customers in the design process also makes it more likely that they'll accept and fully utilize the new system. Gap analysis can be used to find process nuances and peculiarities that call for ERP software modification or adjustments to workflow or processes to fit the ERP system itself better. The team might disclose the gaps to its implementation partner or supplier and request that they suggest potential fixes.
3. Evolution
With precise design specifications, development can start at this implementation stage. The revised procedures must be supported, which involves setting and, when necessary, modifying the software and integrating the ERP with other systems that the business already uses.
The team should develop training materials during software development to help users adjust to the new system. Also, data migration planning needs to start, which frequently entails extracting, processing, and loading data from different systems using different formats, while eliminating duplicate or inconsistent data. In this phase, the project team should choose which data to migrate rather than all historical data at once, much of which needs to be revised.
4. Testing
Concurrent testing and development are possible. Test modules and features might be tested, corrected, and revised based on the findings and retested. Testing a different ERP module while another one is still being developed may be possible. Early testing of the software's fundamental features should be followed by thorough testing of its features, which should include letting some employees use the system for all of their regular tasks. As part of this step, users should receive training and be able to test the updated data.
To start user training, most providers can provide pre- and post-deployment solutions. Although vendor support is important, the company should also utilize the training materials created during the development process. Resources specially tailored to meet your end users' daily tasks also have significant value.
5. Disposition
Your staff may face problems navigating the diverse pieces despite your best efforts to prepare them for the transition. Be prepared for these potential problems and urge your project team to ask questions, explain the system, and try to resolve any issues.
Whenever issues arise, your implementation partner should be able to troubleshoot. It may take some time for users to become accustomed to the system and achieve the productivity gains they desire. While some businesses strive to roll out every module of the ERP system simultaneously, others prioritize specific high-priority modules or activities before gradually adding others. Some companies use traditional methods concurrently with the new ERP implementation to limit risk, even though doing so might increase project costs and decrease user productivity.
6. Updates & Support
Next, it's important to ensure that users are satisfied and the business meets the identified goals. At this phase, the project team may still be in charge of the ERP system, but its attention will now be on gathering user feedback and modifying the system as necessary.
If your ERP system is on-premises, you must deploy software updates regularly and possibly upgrade your hardware. If you use a cloud-based ERP system, your vendor might update the program automatically.
How Do You Choose ERP Software?
The very first stage of the ERP deployment life cycle is choosing an effective ERP package that best suits your organization and your demands after conducting thorough research. A few considerations for successful ERP adoption include the degree of compatibility and customization an ERP system may offer your company, its reliability, and the future assistance of the software vendor.
At this stage of the ERP life cycle, you should develop a precise and practical plan for the procedure. This entails setting project deadlines and timetables and defining roles and responsibilities for the ERP adoption process.
Gap analysis is carried out to develop a complete and transparent model to identify the present condition of the firm and the future course it will take by the organization's business objectives.
ERP Implementation Best Practices
The success of a phased implementation strategy cannot be assured by its creation alone. Following best practices for ERP deployment in each step is equally crucial. Overall, recommended actions include:
- Never undervalue planning. Going into design and development may be tempting, but taking your time during the initial planning and discovery process is essential. By ensuring that the project has high-level support, runs with a clear strategy, and is allotted good money and personnel, this phase should lay the groundwork for the entire implementation project.
- Don't undervalue assistance and instruction. Some project team members could believe that the deployment date marks the completion of the implementation process, failing to give subsequent events enough consideration.
The deployment date is only the beginning for the system's users; the project's sustained success depends on what happens afterward. Planning and dedicating enough resources is crucial to provide technical assistance, resolving problems, and releasing updates. In this situation, end-user training is equally important. Workers should feel confident using the system and familiar with new workflows, especially if an external consultant is not provided by the vendor.
- Planning is critical while migrating data. Some businesses make the error of transferring all historical data to the new system simultaneously. Some of the data in older systems might be redundant or outdated. Is order data from ten years ago valuable? Are all of the vendors on your list still in business?
A clear plan for cleaning up and organizing the organization's data is essential before switching to an ERP system. It makes sense to thoroughly review legacy data, remove dated customer accounts and scan for data errors.
- Communicate: This is crucial at every stage of the implementation process. Whenever possible, the team should communicate with every company employee about the rationale and objectives for the ERP deployment, as well as what to expect at each stage. A two-way conversation is essential: The project team should properly hear users' concerns before and after distribution.
- Be patient. Implementing an ERP system takes time, money, and resource investments, and how you put it into practice will determine how well it functions. Ensure you continue to examine and improve your business processes after the go-live of your ERP. Along with incrementally adding features and functionalities as you go, this can help you develop an effective ERP product in the long run.
Make Your Business Operations Easy with ERP Implementation Cycle
ERP simplifies controlling all departments by using a centralized database, a quick and straightforward working method that takes very little time. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is a core component of automating manufacturing operations for SMEs. Executing all the ERP implementation steps accurately is important, including planning, assessment, implementation, transition, and operations.
TranZact offers advanced ERP solutions along with dedicated implementation support to ensure seamless migration to the cloud platform. It also offers a free trial along with forever free usage of all its base features so that customers can get a complete hands-on of the system.
FAQs on ERP Implementation Life Cycle
1. What is the ERP implementation process?
The phases and steps involved in the deployment of ERP vary, often including:
- Installation settings and options configuration for ERP software.
- Data transfer from the old system regarding transactions and finances.
- Granting users (or workers) access to the ERP system, defining their roles, and configuring their security settings.
- End-user instruction for ERP software.
2. What is the ERP implementation life cycle?
The period needed to establish ERP software within your business is the implementation life cycle. The length of the installation can change depending on your company's complexity, but on the higher side, the lifetime is six to twelve months. TranZact offers dedicated implementation and completes the same within a month's time.
3. Which is the most challenging phase in an ERP implementation?
The planning and discovery stage is the most challenging phase in an ERP implementation process. Persuading individuals throughout the firm to invest the required time and effort and accept a precise project deadline on the new system could also be difficult.
4. How can you avoid ERP implementation delays?
Due to the unrealistic nature of the originally projected timescale, many projects may run past schedule. To avoid this, you must spend time getting the first phase right, including creating a reliable timeline and resource requirement estimate.
5. ERP implementation process has how many phases?
The ERP implementation process has six phases: discovery and planning, design, development, support, deployment, and training.